Bio-degradable cards
Every card imaginable!
|
Bio-degradable cards Every card imaginable! Coronary Artery Disease Essential Information and Management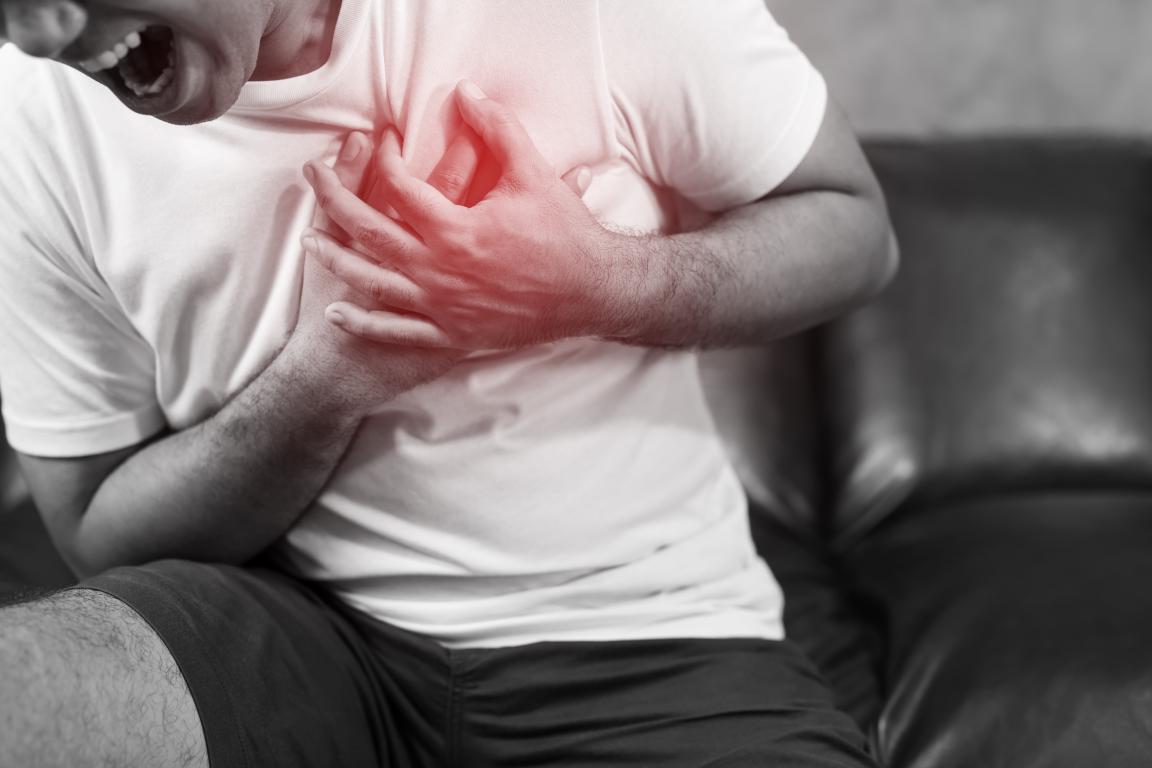
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease: The Basics
What is Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a condition where the coronary arteries, responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the heart, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of fatty deposits, known as plaques. This narrowing reduces blood flow to the heart, which can result in chest pain (angina) and, in more severe cases, lead to heart attacks.
What causes Coronary Artery Disease?The most common cause of CAD is atherosclerosis, a process where cholesterol and other substances accumulate on the artery walls, forming plaques. These plaques can either partially block the arteries or rupture, causing a blood clot that could completely block blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to a heart attack.
How common is Coronary Artery Disease?Coronary Artery Disease is one of the most common heart conditions globally and is a leading cause of death in many countries, including the UK. It primarily affects older adults, but lifestyle factors like poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk even in younger individuals.
Can Coronary Artery Disease be cured?While there is no outright cure for CAD, it can be managed effectively with lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, surgical procedures. Treatment aims to reduce symptoms, prevent heart attacks, and improve quality of life. 
Recognising and Diagnosing Coronary Artery Disease
What are the symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease?Symptoms of CAD often include chest pain or discomfort (angina), which may feel like pressure, squeezing, or fullness in the chest. Other symptoms can include shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, and in some cases, heart palpitations. Some individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms until they suffer a heart attack.
How is Coronary Artery Disease diagnosed?Doctors diagnose CAD through a combination of medical history, physical exams, and diagnostic tests. Common tests include an electrocardiogram (ECG) to check the heart's electrical activity, stress tests to observe heart function under exertion, and imaging tests like coronary angiography to visualize blockages in the coronary arteries.
Who is at risk of developing Coronary Artery Disease?Risk factors for CAD include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and a family history of heart disease. Age and gender also play a role, with men generally at higher risk than women, particularly as they age.
Is stress a factor in Coronary Artery Disease?Yes, stress is considered a risk factor for CAD. Chronic stress can lead to increased blood pressure and other behaviours, such as overeating, smoking, or lack of exercise, which further increase the risk of developing CAD. 
Managing and Treating Coronary Artery Disease
What lifestyle changes can help manage Coronary Artery Disease?Lifestyle changes are crucial in managing CAD. These include adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and high in fruits and vegetables, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, and managing stress. Maintaining a healthy weight and controlling conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure are also essential.
What medications are commonly prescribed for Coronary Artery Disease?Medications for CAD typically aim to reduce symptoms and prevent complications. These can include statins to lower cholesterol, aspirin to reduce blood clotting, beta-blockers to lower heart rate and blood pressure, and nitrates to relieve chest pain. In some cases, doctors may prescribe ACE inhibitors or calcium channel blockers.
What surgical procedures are available for Coronary Artery Disease?When lifestyle changes and medications are insufficient, surgical options might be considered. These include angioplasty, where a balloon is used to open up narrowed arteries, often followed by the placement of a stent to keep the artery open. In more severe cases, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may be performed, where blood vessels from another part of the body are used to bypass blocked arteries.
Can Coronary Artery Disease lead to other complications?Yes, CAD can lead to severe complications if left untreated. These include heart attacks, heart failure, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), and sudden cardiac death. It is crucial to manage the condition effectively to reduce the risk of these life-threatening events. 
Prevention and Long-term Outlook for Coronary Artery Disease
Can Coronary Artery Disease be prevented?While some risk factors like age and family history cannot be changed, many others can be managed or prevented. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, and keeping cholesterol and blood pressure in check can significantly reduce the risk of developing CAD.
How does diet affect Coronary Artery Disease?Diet plays a vital role in both preventing and managing CAD. A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can increase the risk of atherosclerosis. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of CAD.
Is regular exercise important for preventing Coronary Artery Disease?Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining heart health. Exercise helps lower blood pressure, improves cholesterol levels, aids in weight management, and reduces stress. It is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
What is the long-term outlook for someone with Coronary Artery Disease?The long-term outlook for someone with CAD depends on several factors, including how early the disease is diagnosed and how well it is managed. With appropriate lifestyle changes, medications, and possibly surgical interventions, many individuals with CAD can lead a full and active life. However, ongoing management and regular medical follow-ups are crucial to preventing complications.
© 2024 The Card Project Uk Ltd
VAT: 453 2087 06
|