FAST The Lifesaving Method for Identifying Strokes
Disclaimer
This guide is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Stroke is a medical emergency, and symptoms should always be assessed by a qualified healthcare professional. If you suspect someone is having a stroke, call 999 immediately. Always consult your GP or a healthcare provider for any personal health concerns. This information is accurate as of December 2025. We're here to help you understand the basics in a clear way, but remember, every situation is unique, and getting expert help right away is the safest step.
Table of Contents
What is a Stroke and Why Does Time Matter?
It's natural to feel a bit anxious when thinking about strokes, especially if you've known someone affected by one. But gaining knowledge about what they are and how to respond can give you real confidence in handling an emergency. Let's start by explaining the basics in a straightforward way, so you can feel more prepared without getting overwhelmed.
How a Stroke Occurs
A stroke takes place when the blood supply to a part of the brain gets suddenly cut off. This can happen because of a blockage in a blood vessel or due to bleeding from a burst vessel. Without that steady flow of blood, brain cells miss out on the oxygen and nutrients they rely on to function. Over time, those cells begin to die, which is why strokes are sometimes referred to as a "brain attack"—much like how a heart attack impacts the heart. In the UK, around 100,000 people experience a stroke each year, making it a significant health issue that touches many families. Understanding this process helps you see why quick action is so vital, as it directly influences how much recovery is possible.
The Impact on Daily Life
Strokes can lead to lasting changes in a person's abilities, such as difficulties with movement on one side of the body, challenges in speaking clearly, or shifts in how someone thinks and processes information. These effects vary widely depending on which part of the brain is involved and how severe the interruption to blood flow was. It's completely understandable if this sounds worrying, particularly for parents concerned about their children or for those caring for older relatives. However, many people do recover significantly, especially with modern treatments and support from rehabilitation teams. Advances in medical care mean that survivors often regain independence through therapies tailored to their needs. Knowing these outcomes can reassure you that while strokes are serious, they're not always as devastating as they might first seem.
Why Every Minute Counts
Time is absolutely critical during a stroke because the longer brain cells go without oxygen, the more damage occurs—potentially leading to greater long-term challenges. Public health efforts, like the NHS's Act FAST campaign, emphasise recognising symptoms early to start treatment as soon as possible. Paramedics in the UK are well-trained to identify strokes on the scene and rush patients to specialised stroke units where they can receive life-changing interventions. For instance, clot-busting medications can dissolve blockages if given within a few hours, or procedures might physically remove clots to restore blood flow. Even a short delay can result in more extensive brain injury, but prompt care often leads to better recoveries and fewer complications. This focus on speed empowers everyday people like you to make a real difference, whether for a loved one or a stranger.
Types of Strokes Explained
-
Ischaemic Strokes:
These are the most common type, accounting for around 85% of cases in the UK, and they occur when a clot blocks a blood vessel leading to the brain. The clot might form locally or travel from elsewhere in the body, such as the heart. Risk factors like high blood pressure or smoking can contribute to this buildup. Treatments often involve medications to break down the clot or surgical options to clear the vessel. Early detection through methods like FAST can lead to faster interventions, improving chances of minimal long-term effects. It's reassuring to know that with lifestyle changes, many people reduce their risk of this type significantly.
-
Haemorrhagic Strokes:
This type happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing bleeding that puts pressure on surrounding tissues. It's less common but can be more severe due to the rapid buildup of blood. Conditions like uncontrolled high blood pressure or weakened vessel walls from aneurysms are often involved. Immediate medical care focuses on controlling the bleed and reducing pressure in the brain. While recovery can take time, many individuals benefit from specialised care in hospital settings. Understanding the difference helps you appreciate why all strokes require urgent attention, regardless of the cause.
Who Can Be Affected?
Strokes don't discriminate by age—they're more frequent in older adults, but they can strike younger people and even children in rare cases. Factors like family history or certain health conditions might increase the likelihood at any stage of life. If you're a parent or caregiver, it's helpful to know that while uncommon in kids, strokes in younger groups often have good recovery rates with early treatment. Overall, awareness across all ages means more lives saved. This broad impact underscores the importance of community education on signs and responses. By staying informed, you're contributing to a safer environment for everyone around you.
Key Stroke Facts
Here are some important facts about stroke in the UK to help put things into perspective. These highlight why awareness and quick action matter so much. These figures come from the Stroke Association's latest research – you can view the most up-to-date UK stroke statistics here: stroke.org.uk/stroke/statistics
-
Around 100,000 people have a stroke in the UK each year – that's one every five minutes.
-
There are over 1.3 million stroke survivors living in the UK today.
-
Stroke is the fourth leading cause of death in the UK, with about 38,000 stroke-related deaths annually.
-
More than half of stroke survivors are left with a disability, but many go on to make significant recoveries with the right support.
-
Hospital admissions for stroke have risen over the years, partly due to an ageing population and better survival rates.
-
Acting quickly can save brain cells – treatments like clot-busting drugs are most effective within 4.5 hours of symptoms starting.
Breaking Down the FAST Method: Step by Step
If you've ever wondered how to spot a stroke in those critical first moments, the FAST method is your straightforward guide. Developed and promoted by the NHS and the Stroke Association, it's been a cornerstone of stroke awareness in the UK since 2009, with a major refresh launched in November 2024 to tackle ongoing delays in calling 999. It's completely normal to feel a surge of concern in such situations, but having this tool at hand can help you respond with clarity and confidence. What makes FAST so effective is its simplicity—it cuts through the panic and focuses on quick checks that anyone can do, whether you're at home with family or out in public. Over the years, this approach has helped get thousands more people to hospital faster, improving their chances of recovery. The 2024 update highlights that even mild or single symptoms are emergencies, as people often wait an average of 88 minutes before seeking help. Let's walk through it together, exploring each part in detail so you feel equipped to use it if needed.
For the latest Act FAST resources, including information, videos, and downloadable assets, see the official campaign resource page: campaignresources.dhsc.gov.uk
The Origins and Impact of FAST
The FAST campaign has played a vital role in educating the public about stroke recognition, saving lives through quicker responses.
-
How It Started: Launched nationally in 2009 by the Department of Health, FAST was designed based on research showing that a simple, memorable tool could significantly boost how quickly people seek help. It narrowed focus to the three most reliable symptoms plus urgency, making it easy for non-experts to act decisively and reducing hesitation in emergencies.
-
Proven Results: Since its rollout, NHS data shows it has enabled thousands more patients to reach hospital in time for clot-busting treatments, leading to higher survival rates and less severe disabilities overall. For example, early campaigns saw rises in timely arrivals, and ongoing efforts continue to build on this, with more people now surviving strokes than ever before thanks to greater awareness.
-
Recent Updates: The November 2024 refresh addressed persistent delays, with new analysis revealing an average 88-minute wait from symptom onset to calling 999. It strongly emphasises that symptoms can be subtle or isolated—such as slight difficulty smiling—urging no hesitation, a message backed by surveys showing many still wait for multiple signs before acting.
Preparing to Use FAST: Building Confidence Ahead of Time
Getting familiar with FAST before an emergency arises can make all the difference in staying composed and acting swiftly.
-
Why Preparation Helps: Strokes strike suddenly, often leaving little time to process, so occasional mental rehearsals or family discussions turn it into an instinctive response. This is especially useful for parents, caregivers, or those supporting older relatives, helping everyone feel more secure and ready to spot changes quickly.
-
Adapting to Different Situations: In busy or public settings, prioritise visible checks; if someone is alone, they could use a mirror or phone to self-assess. For those whose first language isn't English, rely on gestures or test in their preferred language to spot genuine sudden changes without confusion.
-
Regional Consistency: Whether in England, Scotland, Wales, or Northern Ireland, dialling 999 activates a coordinated stroke response, with ambulances starting preliminary assessments en route to specialised hyperacute stroke units (HASUs) for rapid expert care.
Face: Spotting Facial Weakness
Facial drooping is often the most noticeable early sign of a stroke, making this the perfect starting point for your quick check.
-
Step-by-Step Check: Politely ask the person to smile broadly or show their teeth, then carefully compare both sides for any new asymmetry, such as one side of the mouth or eye failing to lift properly. This sudden change stands out because it's typically one-sided and appears out of nowhere, even if mild.
-
Underlying Cause: It results from disrupted blood flow affecting the brain's control over facial nerves, causing temporary weakness or numbness that impacts expression. Understanding this helps you recognise it's not just tiredness but a potential brain emergency requiring immediate action.
-
Prevalence and Importance: Research from the Stroke Association indicates this occurs in 80-85% of cases, positioning it as one of the most dependable indicators for early detection. Spotting it promptly opens the door to scans and treatments that can preserve facial function and limit wider damage.
-
Special Considerations: In younger people or children (where strokes are rarer but possible), it might show as an uneven cry or difficulty feeding; always compare to their normal appearance. Paramedics rely heavily on this for initial phone triage and fast-tracking to hospital.
-
Common Misconceptions and Tips: Unlike gradual issues from dental problems or past conditions like Bell's palsy, stroke-related drooping is abrupt—trust your instincts and act, as even mild cases, like those featured in the 2024 NHS adverts, have led to successful timely interventions and full recoveries.
Arms: Testing for Limb Weakness
Arm weakness provides a clear, testable clue that something is wrong on one side of the body.
-
Step-by-Step Check: Ask the person to raise both arms to shoulder level or overhead and hold them there briefly; look for one arm drifting down, weakening, or refusing to lift symmetrically. This simple motion highlights imbalances quickly and safely, adapting easily if they're seated.
-
Underlying Cause: The stroke interrupts brain signals to muscles, often causing hemiparesis (one-sided weakness) that can affect arms more noticeably at first. Recognising this link reinforces why a sudden inability to hold objects evenly is a red flag for urgent help.
-
Prevalence and Importance: Present in over 70% of strokes per NHS insights, it's key for ruling out mimics and qualifying patients for procedures like thrombectomy, which can dramatically reduce long-term arm impairment when done early—often within hours of arrival at a specialist unit.
-
Special Considerations: Adapt for seated or lying positions by testing hand squeezes or resistance; in children, it could manifest as sudden dropping of toys or clumsiness in play. This sign is particularly helpful for self-assessment if alone.
-
Common Misconceptions and Tips: Don't confuse it with slow-onset issues like joint pain—stroke weakness hits instantly, and even slight drift counts, preventing delays that could limit recovery options and lead to greater challenges.
Speech: Detecting Communication Issues
Speech changes can reveal stroke involvement in brain language areas, even if physical signs are subtle.
-
Step-by-Step Check: Request the person repeat a straightforward sentence like "The sky is blue today" or answer basic questions; note any slurring, word mix-ups, confusion, or trouble comprehending you. Listening attentively in a calm voice makes this check effective and reassuring.
-
Underlying Cause: Reduced blood supply to regions like Broca's or Wernicke's areas leads to dysarthria (slurred sounds) or aphasia (word struggles), varying from mild to profound. This explains why someone might suddenly sound unclear despite no alcohol or exhaustion.
-
Prevalence and Importance: Affecting around 60% of cases, it's crucial for diagnosis, especially in women or younger adults where it may dominate over physical signs. Early identification supports speech therapy paths that often restore clear communication, improving quality of life post-recovery.
-
Special Considerations: Test in the person's primary language if needed; isolated confusion can still signal stroke. Operators on 999 calls frequently use this to prioritise dispatch and ensure rapid transport.
-
Common Misconceptions and Tips: Abrupt onset distinguishes it from gradual fatigue—if they sound unexpectedly "off" or struggle unusually, proceed without second-guessing, as this has averted worse outcomes in many real-life cases where quick calls led to timely treatment.
Time: Turning Observation into Action
Time is the element that ties FAST together, emphasising urgency once any sign appears.
-
Step-by-Step Check: Immediately record the symptom start time (even approximately) and call 999, clearly describing your observations to the handler who can guide you further. Stay composed—this activates expert help swiftly, with paramedics trained to confirm and rush you to a hyperacute stroke unit.
-
Underlying Cause and Urgency: Delays allow irreversible brain cell loss (estimated at millions per minute); thrombolysis (clot-busting drugs) works best within 4.5 hours, while thrombectomy (clot removal) can extend to 6-24 hours in select cases, making precise onset details invaluable for treatment decisions at specialist centres.
-
Prevalence and Importance: The 2024 campaign highlights that waiting for multiple symptoms halves treatment success odds—one sign alone justifies action, as backed by data showing better recoveries and fewer disabilities with minimal hesitation.
-
Special Considerations: If symptoms fluctuate or resolve briefly, call anyway (possible mini-stroke warning); self-suspecters should not drive but dial directly. Rural responses may take longer, so early alerts help planning and coordination.
-
Common Misconceptions and Tips: Many downplay mild signs hoping they'll pass, but paramedics handle assessments efficiently—better a quick check than regret, turning potential tragedy into manageable care, as seen in survivor stories where prompt calls enabled full recoveries.
What Happens After Calling 999: The UK Stroke Pathway
-
Immediate Response: The call handler assesses details and dispatches a paramedic-trained ambulance; they perform FAST and other checks en route, often starting stabilising care.
-
Arrival at Hyperacute Stroke Unit (HASU): Paramedics bypass standard A&E, taking you directly to one of the UK's specialised HASUs for 24/7 expert care, including urgent brain scans to confirm stroke type.
-
Time-Critical Treatments: If eligible, thrombolysis can be given within 4.5 hours to dissolve clots, or thrombectomy to physically remove them—procedures that significantly reduce disability when timed right.
-
Ongoing Care: After initial stabilisation (often 72 hours in HASU), transfer to an acute stroke unit for rehabilitation, with therapies tailored to needs; many survivors regain independence through this pathway.
-
Reassuring Outcomes: Prompt action often leads to better results—advances mean more survivors than ever, with stories like those in NHS campaigns showing people returning to normal life after fast responses.
Common Pitfalls, Variations, and Extra Tips
-
Why People Hesitate: Worry about "overreacting" or assuming minor causes leads to the average 88-minute lag, yet services are designed for caution with no downside—paramedics prefer thorough checks.
-
Atypical Presentations: Women, younger adults, children, or posterior circulation strokes may show more dizziness, severe headache, confusion, vision changes, nausea, or balance issues rather than classic signs—still warrant 999 if sudden and unexplained.
-
Limitations of FAST: While excellent for most strokes, it can miss some posterior ones (affecting balance or vision)—that's why erring on caution is key; emerging tools like BEFAST add these but FAST remains the core NHS recommendation.
-
Practising Effectively: Free Stroke Association resources, like apps and videos, offer realistic simulations; involve family or schools for broader preparedness and confidence.
-
Sharing the Knowledge: Talking about FAST in communities or workplaces amplifies its reach, contributing to national improvements in response times and outcomes.
By breaking FAST into these clear, detailed checks—with insights into real pathways and outcomes—you now have a robust tool that goes beyond the basics, helping you feel truly prepared and confident in any situation.
Other Possible Signs of Stroke
While the FAST method is excellent for spotting the most common stroke symptoms quickly, it's natural to wonder if there might be other clues—especially since not every stroke affects the face, arms, or speech in the classic way. The NHS and Stroke Association focus strongly on FAST because it catches the majority of cases reliably, but strokes can sometimes involve different parts of the brain, leading to additional or less typical signs. This is particularly true for posterior circulation strokes, which affect the back of the brain and make up about 20% of ischaemic strokes in the UK. It's completely understandable to feel unsure about subtler changes, but knowing these can help you stay vigilant without unnecessary worry. The key message from experts remains: if anything sudden and unexplained happens that affects the brain's normal function, treat it seriously and call 999. Paramedics are trained to sort it out, and it's always better to get checked promptly.
Why FAST Doesn't Catch Every Stroke
FAST is designed to be simple and fast to use in an emergency, focusing on the symptoms that appear in around 70-85% of cases. However, some strokes—especially those in the brainstem, cerebellum, or occipital lobes—can present differently because they impact balance, vision, coordination, or other functions rather than one-sided weakness or speech. Research shows that posterior strokes are misdiagnosed more often initially due to these varied presentations. Women, younger adults, and children may also experience more atypical symptoms. Recognising this doesn't complicate things; it just empowers you to act on any sudden neurological change, even if it doesn't perfectly match FAST.
Additional Signs to Watch For
Here are some other common symptoms that could signal a stroke. These often appear suddenly, just like FAST signs, and may occur alone or alongside them:
-
Sudden Vision Problems — This might include blurred vision, complete loss of sight in one or both eyes, double vision, or a sensation like a curtain coming down over your field of view. It happens when blood flow to the visual areas at the back of the brain is disrupted. Vision changes are particularly common in posterior strokes and can be the only sign in some cases. If you're helping someone, ask if things look odd suddenly—this has prompted timely calls in many situations. Early action here can preserve sight and prevent further damage.
-
Dizziness, Loss of Balance, or Coordination Issues — Feeling severely unsteady, like the room is spinning (vertigo), trouble walking in a straight line, or sudden clumsiness without an obvious reason. These stem from impacts on the cerebellum or brainstem, which control balance and movement. Up to 10% of cerebellar strokes present mainly with nausea, vomiting, and dizziness, mimicking inner ear problems. It's easy to dismiss as a bug or dehydration, but if it's abrupt and severe, especially with other hints, call 999—delays can lead to falls or worse outcomes.
-
Severe Sudden Headache — Often described as the worst headache ever, sometimes with neck stiffness or vomiting; this is more linked to haemorrhagic strokes or dissections. While not every bad headache is a stroke, a thunderclap onset (reaching peak intensity quickly) warrants urgent attention. In posterior strokes, headache occurs in up to 30% of cases, adding to diagnostic challenges.
-
Sudden Confusion or Altered Mental State — Becoming disoriented, struggling to understand what's happening, memory lapses, or unusual behaviour changes without clear cause. This can indicate involvement of areas controlling awareness or cognition. In some posterior strokes, it might include drowsiness or agitation.
-
Nausea, Vomiting, or General Weakness — Persistent sickness combined with other signs, or overwhelming fatigue/weakness not limited to one side. Women sometimes report more generalised symptoms like nausea, hiccups, shortness of breath, or chest pain alongside or instead of classic ones.
Variations in Different Groups
Symptoms can differ based on age, gender, or stroke location, which is why awareness helps tailor your response:
-
In Women → Research highlights that women may experience more non-classic signs, such as general fatigue, nausea, confusion, or hiccups. Hormonal factors like pregnancy or HRT can influence risk, and strokes in women often occur later in life.
-
In Children and Younger Adults → Though rare (around 400 childhood strokes yearly in the UK), signs might include sudden seizures, irritability, feeding difficulties in babies, or headaches alongside weakness. In older kids, it could mimic migraines or seizures—always seek urgent review if unexplained.
-
Posterior Circulation Specifics → These strokes often cause vertigo, double vision, swallowing difficulties, or crossed symptoms (e.g., face one side, body the other). They carry higher risks if untreated but good recovery potential with fast care.
When to Act and Why It Matters
If you notice any sudden change in how someone sees, balances, thinks, or feels—especially if it comes on abruptly—don't wait for it to match FAST perfectly. The Stroke Association and NHS advise calling 999 anyway, as symptoms can fluctuate or start mildly. Even if they resolve quickly, it could be a warning sign needing scans. Reassuringly, many people make excellent recoveries when help arrives fast, and paramedics handle assessments expertly. By staying alert to these possibilities, you're adding an extra layer of protection for yourself and loved ones without overcomplicating the core message: at the first unusual sign, time to call 999.
The Stroke Association has helpful guides on recognising all stroke symptoms: You can see more on their website stroke.org.uk
What to Do If You Suspect a Stroke
Spotting the signs of a stroke is crucial, but knowing exactly what to do next can truly make the difference between a strong recovery and lasting challenges. It's completely understandable to feel panicked in that moment—your quick, calm actions can save brain function and even a life. The NHS and Stroke Association emphasise that stroke is a medical emergency, and acting fast gets the person to specialist care where time-sensitive treatments can limit damage. Every minute counts, as brain cells start to die without blood flow, but modern UK stroke services are designed for rapid response. Let's go through the steps clearly, so you feel prepared to handle this if it happens to a loved one, a stranger, or even yourself.
Immediate Steps: Stay Calm and Act Quickly
If you notice any sudden changes—like those from FAST or other signs—don't wait to see if they improve. Here's what to do right away:
-
Call 999 Without Delay — Tell the operator you suspect a stroke and describe the symptoms clearly. This flags it as a high-priority call, alerting paramedics trained in stroke recognition. They may ask questions to confirm over the phone and can start guiding you. In the UK, saying "suspected stroke" ensures the ambulance is dispatched urgently and pre-alerts the hospital stroke team.
-
Note the Time Symptoms Started — Try to pinpoint when the signs first appeared (or the last time the person was known to be well). This "onset time" is vital information for doctors—it determines eligibility for treatments like clot-busting drugs (thrombolysis, best within 4.5 hours) or clot removal (thrombectomy, possible up to 6-24 hours in some cases). Even an approximate time helps; share it with the operator and paramedics.
-
Stay with the Person and Reassure Them — Keep them calm by saying things like, "Help is on the way—you're doing really well, just stay still." Anxiety is common, and your steady presence can make a big difference. Help them sit or lie down comfortably, but avoid moving them unnecessarily if they're unsteady.
-
Avoid Giving Anything by Mouth — Do not offer food, drink, water, or any medication (even aspirin unless advised by the operator). Stroke can affect swallowing, raising the risk of choking or aspiration, which could worsen things.
-
If the Person Becomes Unconscious — Check if they're breathing normally. If not, the 999 operator will guide you through CPR. If they are breathing but unresponsive, gently place them in the recovery position (on their side with head tilted back) to keep the airway clear, but only if it's safe to move them.
If You're Experiencing Symptoms Yourself
It's tough, but if you think you're having a stroke—perhaps noticing sudden weakness, slurred speech, or vision changes—call 999 immediately, even if alone. Don't drive or ask someone else to take you; paramedics can start care on the scene. Lock the door behind them if possible for safety, and sit down to avoid falling. Many survivors share how making that call themselves led to prompt treatment and better outcomes.
What Happens Next: The UK Stroke Care Pathway
Once you call 999, the system kicks into gear quickly—here's a reassuring overview of the process:
-
Paramedic Arrival and On-Scene Assessment — UK ambulances are equipped for stroke emergencies. Paramedics will perform FAST and other checks, stabilise the person (e.g., oxygen if needed), and often start initial treatments. They'll note your onset time and symptoms for the hospital.
-
Direct Transport to a Specialist Unit — Rather than a general A&E, paramedics take suspected stroke patients straight to a Hyperacute Stroke Unit (HASU)—these are 24/7 specialist centres across the UK with expert teams, rapid scans, and advanced treatments. This bypass saves crucial time.
-
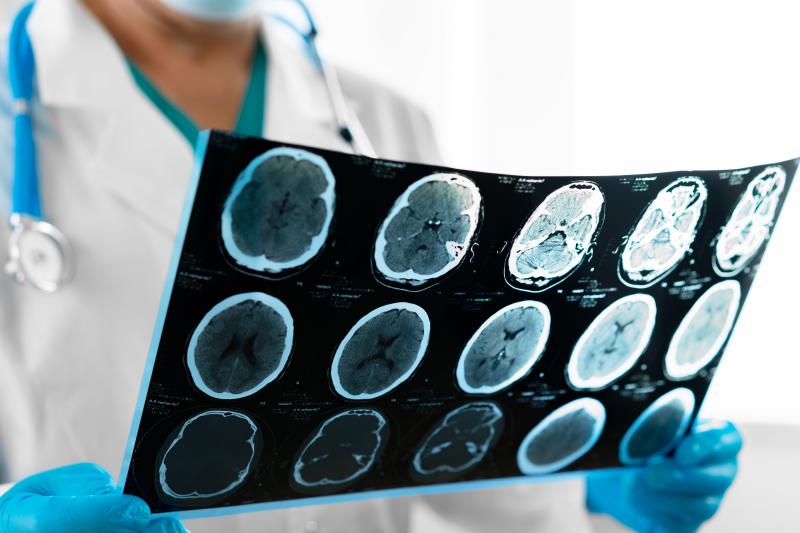
Hospital Arrival and Urgent Tests — Within minutes of arrival, you'll get a brain scan (usually CT) to confirm stroke type and rule out bleeds. Blood tests and monitoring follow quickly.
-
Time-Critical Treatments — If it's an ischaemic stroke (blockage), eligible patients may receive thrombolysis (clot-dissolving injection) or thrombectomy (mechanical clot removal via catheter). These can dramatically reduce disability—thousands benefit yearly thanks to faster pathways. For haemorrhagic strokes, care focuses on controlling bleeding and pressure.
-
Ongoing Specialist Care — After initial treatment (often 72 hours in HASU), transfer to an acute stroke unit for monitoring, therapies, and rehabilitation planning. Multidisciplinary teams (doctors, nurses, therapists) tailor support to needs.
Even If Symptoms Improve or Come and Go
Don't hesitate—call 999 anyway. Transient symptoms could be a transient ischaemic attack (TIA or "mini-stroke"), a warning that a full stroke is imminent. Quick assessment prevents bigger events, often with medication started soon after. Many people regret waiting, thinking it was "nothing," only to face worse later.
Why Quick Action Leads to Hopeful Outcomes
It's natural to worry, but stories from UK survivors highlight how bystanders or family members calling 999 promptly turned scary moments into recoveries. Advances mean more people survive and regain independence than ever—prompt care can save millions of brain cells per minute. Paramedics and hospitals handle "false alarms" expertly, so err on the side of caution. By knowing these steps, you're empowering yourself to help in a real emergency.
Understanding Transient Ischaemic Attacks (Mini-Strokes)
It's worrying to hear about something called a "mini-stroke," especially if you've experienced unusual symptoms that seemed to pass quickly. Many people feel relieved when things return to normal, but a transient ischaemic attack (TIA) is a serious signal from your body that needs attention right away. Often referred to as a mini-stroke, a TIA happens in the same way as a full stroke—through a temporary disruption in blood flow to the brain—but the key difference is that symptoms usually resolve completely within minutes to hours, and there's no permanent brain damage visible on scans. This doesn't make it less important; in fact, it's often described as a "warning stroke" because it significantly raises the risk of a major stroke soon after. The good news is that with prompt medical assessment and treatment, this risk can be greatly reduced, and many people go on to manage their health effectively without further events.
What Causes a TIA and How It Differs from a Full Stroke
A TIA occurs when a small blood clot or debris briefly blocks a blood vessel supplying the brain, cutting off oxygen temporarily. Unlike a full stroke, where the blockage persists and causes lasting damage, the clot usually dissolves or moves on quickly in a TIA. Symptoms are identical to those of a stroke—often matching the FAST checks like facial drooping, arm weakness, or speech difficulties—but they typically last less than an hour (though sometimes up to 24 hours by definition). Brain scans, such as MRI, usually show no permanent injury, which is why it's "transient." However, modern understanding views TIA on a spectrum with stroke; some TIAs may leave tiny unseen effects, but the main concern is the underlying cause, like narrowed arteries, irregular heart rhythms (such as atrial fibrillation), or high blood pressure.
Recognising the Symptoms
Symptoms of a TIA come on suddenly and can include any of the classic stroke signs, plus others:
-
Classic FAST Signs → Facial weakness (e.g., drooping smile), arm or leg weakness (especially one side), speech slurring or difficulty finding words. These resolve but indicate the same urgent issue.
-
Vision Changes → Sudden blurred vision, loss in one or both eyes, or double vision—common if the blockage affects visual pathways.
-
Balance and Coordination Problems → Dizziness, unsteadiness, or trouble walking, sometimes feeling like vertigo.
-
Other Neurological Changes → Numbness, confusion, severe headache, or brief loss of consciousness.
These can vary, and in some groups—like women or younger people—symptoms might lean towards nausea, general weakness, or confusion rather than obvious one-sided issues. If symptoms fluctuate or disappear quickly, it's still likely a TIA.
The Risk of a Full Stroke After a TIA
This is where TIAs earn their "warning" label—without treatment, the chance of a major stroke is highest in the early days:
-
Short-Term Risk → Nearly half of the subsequent stroke risk can occur within the first 48 hours, with overall early risks (within days to weeks) historically as high as 10-20% in older studies, though modern urgent care has lowered this significantly.
-
Longer-Term Outlook → Around 10% risk in the first year, but prompt intervention (medications, lifestyle changes) can cut this dramatically—many people reduce it to near normal levels.
-
Reassuring Progress → Thanks to better awareness and rapid clinics, stroke rates after TIA have fallen in recent years; for instance, urgent specialist assessment prevents many events.
It's understandable to downplay resolved symptoms, but ignoring a TIA is one of the biggest risks—treating it as a wake-up call empowers you to prevent worse outcomes.
What to Do If You Suspect a TIA
Even if symptoms have fully gone, act urgently—don't wait:
-
If Symptoms Are Ongoing → Call 999 immediately; treat it exactly like a stroke.
-
If Symptoms Have Resolved → Contact your GP straight away or call 111 for advice. NHS guidelines recommend specialist assessment within 24 hours of symptoms starting, often at a dedicated TIA clinic.
-
Why Urgency Matters → Rapid evaluation identifies causes (e.g., carotid artery narrowing needing surgery, or atrial fibrillation requiring blood thinners) and starts prevention quickly.
Diagnosis and Treatment in TIA Clinics
UK services prioritise TIAs with fast-track pathways:
-
Initial Checks → Brain scan (CT or MRI), carotid ultrasound, heart monitoring (ECG), blood tests.
-
Risk Assessment → Specialists evaluate causes; tools like the Canadian TIA Score help guide urgency, though all suspected TIAs get prompt review.
-
Common Treatments → Antiplatelet drugs (e.g., aspirin or clopidogrel) started immediately to prevent clots; statins for cholesterol; blood pressure control. If severe artery narrowing found, procedures like carotid endarterectomy can be life-changing.
-
Lifestyle Support → Advice on quitting smoking, healthy eating, exercise—often with referrals to support programmes.
Many clinics complete investigations in one visit, providing peace of mind and a clear plan.
Long-Term Management and Hopeful Outlook
A TIA is a chance to address underlying risks proactively. With medication adherence and changes (e.g., managing blood pressure, diabetes), most people significantly lower their stroke odds and live full lives. Emotional impacts like anxiety are common—talk to your GP or Stroke Association helpline for support. Driving rules apply too: inform DVLA and avoid driving for at least one month. By treating a TIA seriously, you're taking control—many survivors of potential major strokes credit quick action after their "mini" warning for their good health today.
Risk Factors, Prevention, and Long-Term Outlook
It's natural to feel concerned about stroke risks, especially if there's a family history or you've noticed changes in your health. But the encouraging truth is that up to 90% of strokes are preventable through managing risk factors and making practical lifestyle adjustments. In the UK, while hospital admissions for stroke have risen over recent years—partly due to an ageing population and better detection—death rates have fallen significantly, and more people than ever are surviving and recovering well. Advances in prevention, rapid treatment, and rehabilitation mean that focusing on what you can control really does make a difference. Whether you're worried for yourself, a parent, or a partner, understanding these factors empowers you to take positive steps with support from your GP.
Understanding Stroke Risk Factors
Stroke risks are a mix of things you can't change and those you can influence. High blood pressure remains the single biggest modifiable risk factor, contributing to around half of all strokes.
-
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk →
-
High blood pressure (hypertension) damages blood vessels over time, making clots or bleeds more likely—regular checks at your GP can catch it early.
-
Diabetes affects blood vessels and raises clot risk; good control through diet, exercise, or medication helps a lot.
-
High cholesterol builds up plaque in arteries, narrowing them—statins prescribed by your doctor can lower this effectively.
-
Atrial fibrillation (an irregular heartbeat) allows clots to form in the heart, which can travel to the brain; blood-thinning medications like anticoagulants prevent this in most cases.
-
Lifestyle-Related Risks →
-
Smoking doubles your stroke risk by damaging vessels and raising blood pressure—quitting, even later in life, quickly reduces this, with support available via NHS Stop Smoking services.
-
Being overweight or obese strains the heart and increases related conditions like diabetes; gradual changes add up.
-
Excessive alcohol raises blood pressure; sticking to 14 units a week, spread out, is the guideline.
-
Factors You Can't Change →
-
Age plays a big role—risk rises after 55, but strokes can happen younger too.
-
Family history or genetics can increase likelihood if close relatives had strokes early.
-
Ethnicity matters: people from South Asian, African, or Caribbean backgrounds often face higher risks due to greater prevalence of hypertension and diabetes—earlier screening is recommended.
Many risks overlap, so managing one often helps others—your GP can assess your personal profile with tools like the QRISK score.
Practical Steps for Prevention
Prevention isn't about perfection; small, sustainable changes backed by medical support can significantly lower your chances. NHS guidelines emphasise regular health checks, especially over 40.
-
Healthy Eating Habits → Aim for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins—think Mediterranean-style with plenty of fish, nuts, and olive oil. Cut down on salt (aim for under 6g a day) to help blood pressure, and limit saturated fats from processed foods. Portion control supports weight management without feeling restrictive.
-
Staying Active → Adults should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity a week, like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming—break it into 10-minute bursts if easier. Strength exercises twice a week help too. If you're starting out, your GP can suggest safe ways or refer to local programmes.
-
Quitting Smoking and Moderating Alcohol → Stopping smoking brings benefits within weeks; free NHS support includes apps, helplines, and patches. Keep alcohol moderate—spread units over the week with alcohol-free days.
-
Regular Health Checks and Medications → Get blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes checked regularly—If you're aged 40–74 in England, you can book a free NHS Health Check to assess your stroke and heart risk: see their website for more details on how to do this. If needed, medications like antihypertensives or statins are highly effective when taken as prescribed. For atrial fibrillation, anticoagulants are a game-changer.
-
Other Helpful Measures → Manage stress through relaxation or hobbies, and maintain good sleep—both indirectly support heart health.
These steps have contributed to falling stroke death rates in the UK despite rising admissions.
Long-Term Outlook After a Stroke
The outlook for stroke survivors has improved dramatically—more people survive, and many regain independence thanks to specialist units and rehab.
-
Survival and Recovery Rates → Around 90,000 people survive a stroke each year in the UK, adding to over 1.3 million survivors. While more than half experience some disability initially, intensive rehabilitation helps many improve significantly over months or years. Younger survivors (under 65) often have better recovery potential due to fewer other health issues.
-
Rehabilitation and Support → Early therapy in stroke units—physiotherapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy—maximises gains. Community teams continue this at home, focusing on daily skills. Emotional support addresses common issues like low mood.
-
Living Well Long-Term → Many return to work, driving, or hobbies with adaptations. Ongoing secondary prevention (medications, lifestyle) reduces recurrence risk by up to 80% in some cases. Regular reviews catch needs early.
-
Challenges and Hope → Some face lasting effects like mobility issues or fatigue, but aids, adaptations, and support groups help. Research into new therapies brings ongoing improvements.
Focusing on controllable risks offers real reassurance—talk to your GP for personalised advice, and remember, positive changes at any stage make a meaningful impact.
Conclusion
Thank you for taking the time to read through this guide. Strokes can feel frightening, especially when you think about the sudden way they can appear or how they might affect someone you care about. But the most important thing to carry away is this: you now have clear, practical tools to recognise the signs and act quickly. The FAST method—Face, Arms, Speech, Time—gives you a simple, reliable way to spot the majority of strokes in seconds, and knowing the other possible signs means you’re even better prepared to respond if something looks different. Calling 999 at the first suspicion really can save brain cells, reduce disability, and in many cases, help someone return to the life they love.
The reassuring reality is that stroke care in the UK has improved enormously. Specialist hyperacute stroke units, faster ambulance response, clot-busting drugs and mechanical clot removal are all available when people reach hospital quickly. More people survive strokes today than ever before, and many go on to make excellent recoveries with the right support. Even a transient ischaemic attack (TIA)—once dismissed as “just a funny turn”—is now treated as a valuable warning sign, and urgent assessment can prevent a full stroke in the vast majority of cases.
You don’t have to do everything perfectly to make a difference. Checking your blood pressure occasionally, eating a little more fruit and veg, moving more, stopping smoking, or simply knowing who to call if something seems off—these small steps add up. And if a stroke does happen, the NHS pathway is built to give every eligible person the best possible chance at a good outcome.
If you have any concerns about your own health or someone else’s, speak to your GP or call 111 for advice. In an emergency, always call 999. For further support, information, or to speak to someone, visit the Stroke Association: or call their helpline on 0303 3033 100.
This guide was last updated in December 2025. Stroke care and statistics can change, so always check official NHS or Stroke Association sources for the latest information.
© 2024 The Card Project Uk Ltd
VAT: 453 2087 06
|