Bio-degradable cards
Every card imaginable!
|
Bio-degradable cards Every card imaginable! Life with Lupus Navigating Symptoms Flares and Everyday Challenges
Understanding Lupus: Common Questions AnsweredLupus is a long-term autoimmune condition that can affect various parts of the body. It’s often misunderstood, and many people have questions about what it really means to live with Lupus. In this blog, we’ll answer some of the most commonly asked questions, providing clear and easy-to-understand responses to help clarify the condition. 
What is Lupus and How Does it Affect the Body?
What is Lupus?Lupus is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues. This can cause inflammation and damage to various organs, such as the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, and brain. There are different types of Lupus, with the most common being Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE).
How is Lupus Diagnosed?Diagnosing Lupus can be challenging because its symptoms are often similar to other conditions. There is no single test for Lupus, so doctors usually rely on a combination of blood tests, urine tests, and a review of symptoms. The most common test is the antinuclear antibody (ANA) test, but a positive result alone does not confirm Lupus.
What Causes Lupus?The exact cause of Lupus is still unknown, but it is believed to be the result of a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. People with a family history of autoimmune diseases are at a higher risk, and triggers such as sunlight, infections, and certain medications may also play a role in causing or worsening symptoms.
What are the Early Symptoms of Lupus?Early signs of Lupus can be quite varied. The most common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes (particularly a butterfly-shaped rash across the nose and cheeks), and fevers. These symptoms often come and go, making Lupus difficult to detect in its early stages.
Managing Lupus Symptoms and Flares
What are Lupus Flares?Lupus flares refer to periods when symptoms suddenly worsen. These can range from mild to severe and may involve an increase in joint pain, skin rashes, or inflammation in organs like the kidneys. Managing stress and following a treatment plan can help reduce the frequency and intensity of flares.
How is Lupus Treated?There is no cure for Lupus, but it can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes. Treatment typically includes anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling, corticosteroids to control inflammation, and immunosuppressants to prevent the immune system from attacking healthy tissues. Each person’s treatment plan is tailored to their specific symptoms.
Can Diet Help Manage Lupus Symptoms?While no specific diet can cure Lupus, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health and reduce inflammation. Some people with Lupus find that avoiding foods that trigger inflammation, such as processed meats and sugary snacks, can help manage their symptoms. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, can also have anti-inflammatory benefits.
Can Stress Trigger Lupus Flares?Stress is a well-known trigger for Lupus flares. Emotional and physical stress can cause the body to release hormones that lead to inflammation and worsen symptoms. It’s important for people with Lupus to find ways to manage stress, such as practising relaxation techniques, getting enough rest, and maintaining a regular routine.
Daily Life and Living with Lupus
Can Lupus Affect Mental Health?Living with a chronic condition like Lupus can take a toll on mental health. People with Lupus are more likely to experience anxiety, depression, and mood swings, often due to the physical and emotional stress of managing their symptoms. Support from family, friends, and mental health professionals can be invaluable in coping with these challenges.
Can People with Lupus Work and Lead Normal Lives?Many people with Lupus are able to work and lead full lives, but it often depends on the severity of their symptoms. Lupus can cause fatigue, joint pain, and other issues that make it difficult to maintain a typical work routine. Some people may need to make adjustments, such as working part-time or from home, to accommodate their health needs.
Is Lupus More Common in Women than Men?Yes, Lupus is far more common in women than in men, particularly those of childbearing age. In fact, around 90% of people diagnosed with Lupus are women. Hormonal factors are thought to play a role in this, as Lupus often worsens during pregnancy or after childbirth.
Is Lupus Contagious?Lupus is not contagious. It cannot be spread from person to person through physical contact, sharing food, or being in close proximity to someone who has the condition. Lupus develops from a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and its triggers are not related to contagious diseases.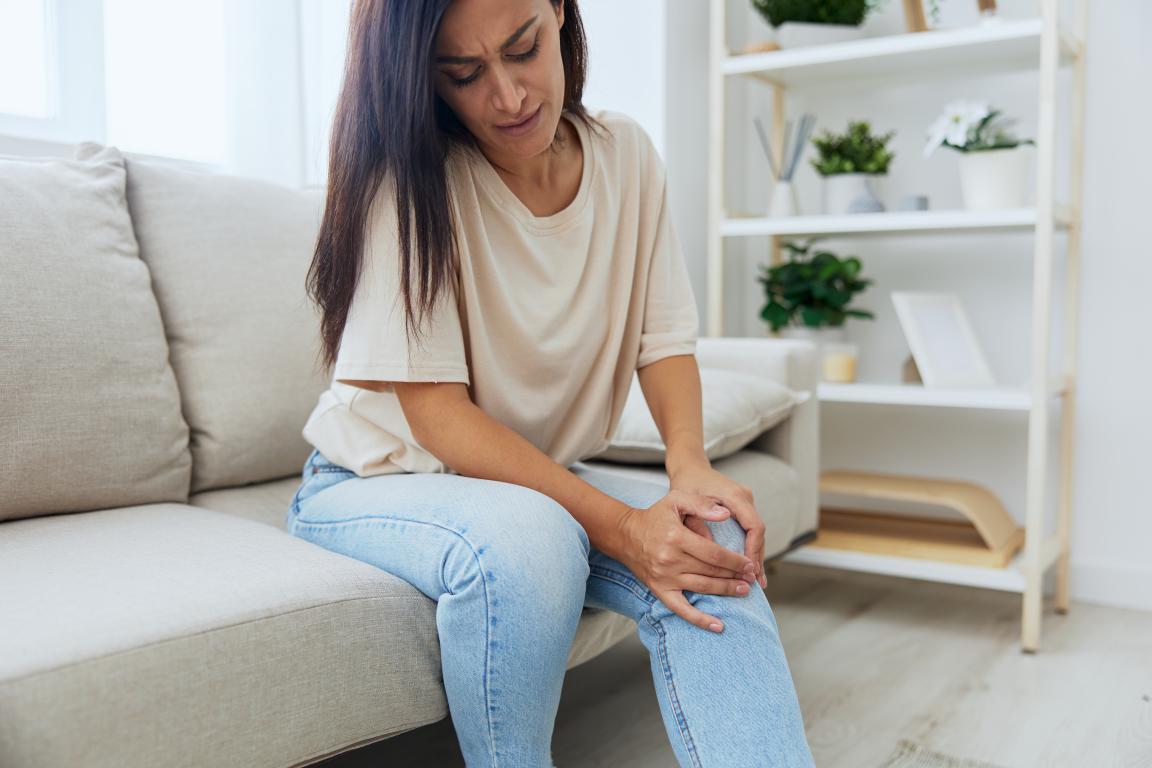
Long-Term Effects and Lupus Complications
Can Lupus Cause Organ Damage?Lupus can affect nearly any organ in the body, leading to complications if not properly managed. The kidneys are particularly vulnerable, and many people with Lupus develop a condition called Lupus nephritis, which causes inflammation in the kidneys. Other organs, such as the heart and lungs, can also be affected by Lupus-related inflammation.
Can Lupus Be Fatal?Although Lupus can lead to life-threatening complications, advances in treatment have significantly improved life expectancy. With proper care and management, many people with Lupus are able to live long, healthy lives. However, untreated Lupus can cause serious damage to the kidneys, heart, lungs, and other vital organs, which can be fatal.
How Does Lupus Affect Pregnancy?Women with Lupus can have successful pregnancies, but they are considered high risk. Lupus symptoms may worsen during pregnancy, and there is a higher chance of complications such as pre-eclampsia and premature birth. It’s essential for women with Lupus to work closely with their doctors to manage their condition during pregnancy.
Are There Different Types of Lupus?Yes, there are several types of Lupus. The most common form is Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), which affects multiple organs and systems in the body. Cutaneous Lupus affects only the skin, causing rashes and lesions. Drug-induced Lupus is a temporary form of Lupus triggered by certain medications, and it usually subsides once the medication is stopped. Lastly, Neonatal Lupus is a rare condition that affects newborns of mothers with Lupus, though most cases are temporary.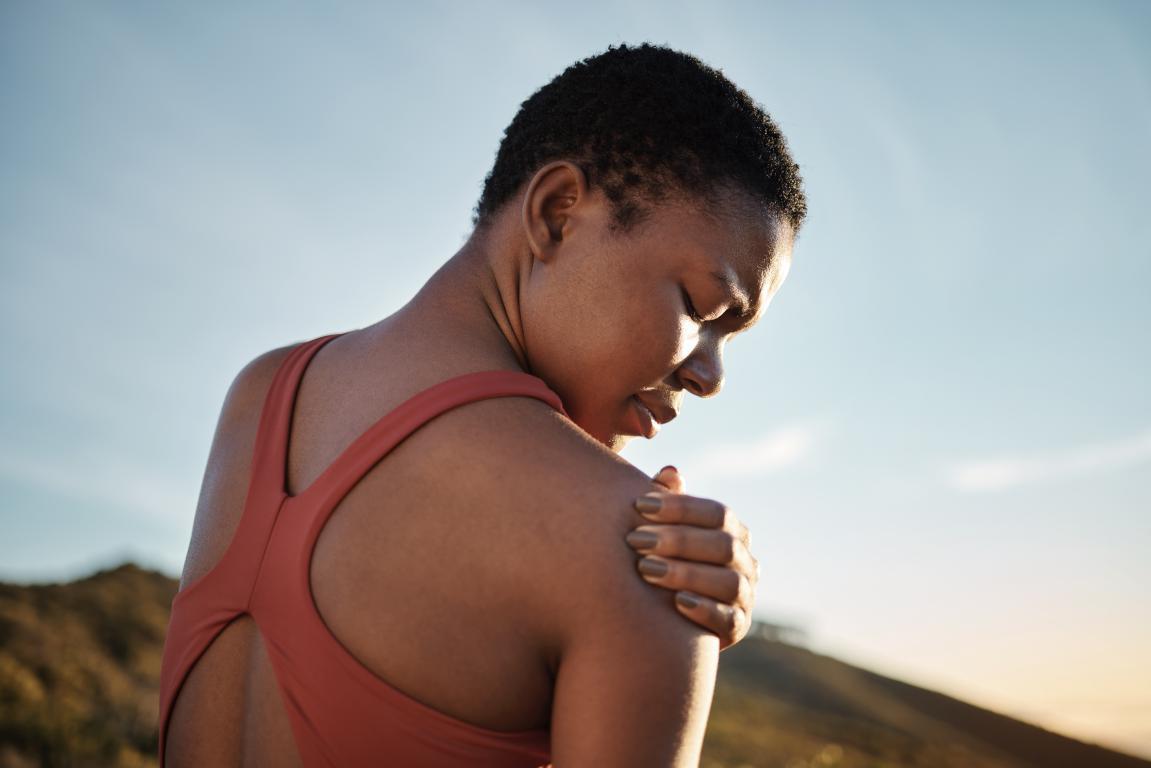
© 2024 The Card Project Uk Ltd
VAT: 453 2087 06
|