Bio-degradable cards
Every card imaginable!
|
Bio-degradable cards Every card imaginable! Exploring the Benefits and Safety of Metal Implants
Safety and Basic Understanding of Metal Implants
What Are Metal Implants?Think of metal implants as sophisticated replacement parts or internal support structures for your body. They are medical devices surgeons use to stabilize, replace, or reinforce damaged bone or joints that are no longer working correctly due to injury, disease, or just old age and wear-and-tear. These implants come in a huge variety of shapes and sizes, depending on where they are needed:
The crucial thing is that these materials are specially selected to be "biocompatible," which is just a fancy way of saying your body won't reject them and they can exist peacefully inside you for a very long time.
Are Metal Implants Safe?For the vast majority of people, metal implants are considered very safe, and they are a standard, successful treatment that dramatically improves quality of life. The materials used, primarily titanium, stainless steel, or cobalt-chrome alloys, have been specifically chosen and developed because they are strong and they won't corrode or cause an inflammatory reaction in your body. Before an implant is ever used, it has to go through extremely strict and rigorous testing and approval processes by government agencies like the FDA. This ensures that the design is sound, the materials are safe, and the manufacturing is consistent. However, "safe" doesn't mean "zero risk." Like any surgery or device, there are always potential issues that your doctor will discuss with you. These can include a small risk of infection, the possibility of the implant loosening over many years, or, very rarely, an allergic reaction to one of the metal components. Being informed and talking openly with your surgeon about your health history is the best way to ensure the highest degree of safety for your specific situation.
Are Dental Implants Metal?Yes, the part of a dental implant that is actually screwed into your jawbone is almost always metal—specifically, titanium. Titanium is the gold standard for dental and orthopedic implants because it has a unique ability to physically fuse with the surrounding bone in a process called osseointegration. This creates an incredibly strong, long-lasting anchor, just like the root of a natural tooth. Sometimes, people who have metal sensitivities or just prefer a metal-free option might look into ceramic implants, which are typically made of zirconia. These are becoming more popular, but titanium is still the material with the longest and most successful track record.
Are Metal Implants Magnetic?For most people, the simple answer is no, your metal implant is not magnetic in a way that will cause problems. This is because modern, commonly used implant materials—especially titanium and its alloys—are non-ferromagnetic. In plain English, that means they are not attracted to magnetic fields. This is a really important point when it comes to having an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan. Since an MRI uses a powerful magnet, doctors need to know what's in your body.
The takeaway is this: always tell your medical team that you have an implant before an MRI, and if possible, carry an implant identification card that specifies the exact material.
Why Do Metal Implants Hurt When It Rains?This is one of the most common and puzzling complaints that people with metal implants or old fracture sites report. The short answer is that no one has a definitive, proven scientific explanation for it, but the discomfort is very real for many people. The most widely accepted theory points to changes in barometric pressure. Barometric pressure is the "weight" of the air pressing down on us, and it often drops right before a storm or rain.
Another potential factor is simply that people tend to be less active and more aware of their body on cold, damp days, which can make them notice a persistent ache more readily. While science doesn't fully explain it, you are definitely not imagining it—it's a phenomenon that doctors hear about all the time. 
Compatibility with Medical Procedures and Disease Risks
Can Metal Implants Cause Autoimmune Disease?This is a really important question that concerns many people, and it’s one that researchers have looked into carefully. Right now, there is no strong, definitive evidence that having a standard metal implant directly causes a new autoimmune disease in a person. The confusion sometimes comes from a related, but different, issue: metal allergy or sensitivity. A very small percentage of people can have an inflammatory response to a specific metal, most commonly nickel (which is sometimes in stainless steel or cobalt-chrome alloys). This reaction is localized—meaning it happens right around the implant site—and it is not the same thing as a systemic autoimmune disease where your body attacks its own tissues everywhere. Here’s how to think about it:
Ultimately, for the vast majority of patients, the proven benefits of a necessary implant far outweigh this theoretical or very rare risk.
Is It Safe to Have an MRI with Metal Implants?For most modern implants, the answer is a reassuring yes, it is safe to have an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging). However, you should never assume and always speak up. An MRI machine uses a powerful magnet and radio waves to create detailed images of your organs and tissues. The primary concern is whether the metal in your body will react to that magnetic field.
Because of these differences, medical professionals need to know the exact material. You should always:
Can Your Body Reject Metal Implants?It is extremely rare for the body to "reject" a modern metal implant in the way it might reject a transplanted organ. Organ rejection is an aggressive, system-wide immune attack. With metal implants, the issue is not typically rejection, but rather a mechanical or infectious problem. Here are the issues that can happen:
Following your surgeon's pre- and post-operative instructions—especially concerning wound care and limiting activity during the initial healing phase—is the best defense against complications.
Can You Go Through Airport Security with Metal Implants?Yes, you can absolutely go through airport security with metal implants. This is an incredibly common occurrence, and security personnel are well-trained to handle it. Since your implant is made of metal, there is a very high probability that it will set off the metal detector, especially large implants like a hip or knee replacement. Don't worry about it—it’s just a fact of life now. Here are a few tips to make the process smoother:
Do not try to hide the fact that you have an implant; just be prepared for the detector to go off, and the staff will take it from there. 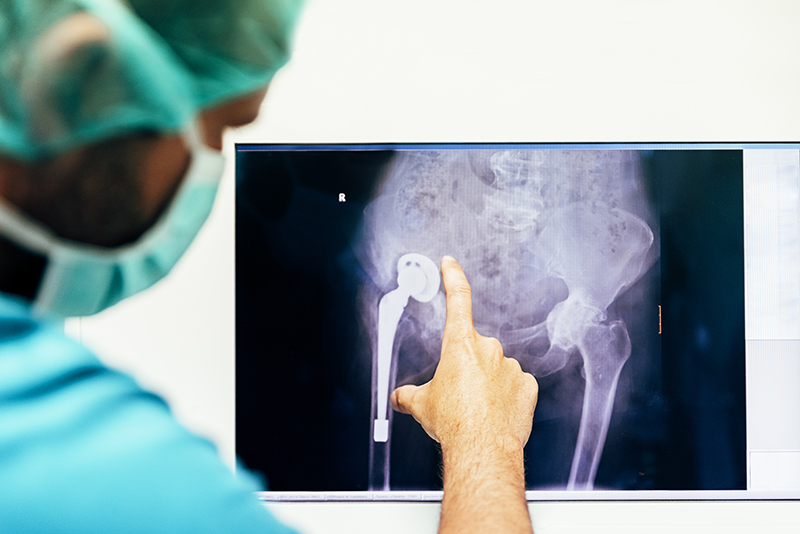
Impact on Medical Imaging and Cancer Risks
Can You Have a CT Scan with Metal Implants?Yes, you can absolutely have a CT scan (Computed Tomography) with metal implants. Unlike an MRI, which uses powerful magnets, a CT scan uses X-rays. Metal implants do not pose a safety risk during a CT scan; they will not move, heat up, or cause harm. However, the metal can create a problem for the image itself, and this is called an artifact.
Modern CT machines and software have special settings and algorithms designed to help reduce these metal artifacts, often called "metal suppression." If your doctor needs a scan near your implant, they will work with the radiology team to use these techniques to get the clearest picture possible.
Do Metal Implants Set Off Metal Detectors?In short, yes, they absolutely can, and often do. Whether the detector goes off depends mainly on two factors: the size of the implant and the sensitivity level of the specific metal detector you walk through.
Don't let this cause you any stress. Security staff see this constantly, and as mentioned before, the best approach is to simply let them know you have an implant when the detector goes off. If you are concerned about privacy, you can often request a private screening.
Do Metal Implants Cause Cancer?This is one of the most reassuring questions to answer: there is no credible scientific evidence or research to suggest that the metals used in medical implants cause cancer in humans. This is a key reason why certain materials are chosen for use inside the body. Before any material is approved for an implant (like titanium, cobalt-chrome, or surgical stainless steel), it is put through years of rigorous testing by regulatory bodies around the world. These tests specifically check for:
The materials that pass these tests are considered "biologically inert," meaning they do not react with the surrounding body tissues in a way that would trigger cell changes or the development of a tumor. The use of these materials in millions of successful surgeries over decades has only reinforced their safety profile.
How Long Do Metal Implants Last?This is not a one-size-fits-all answer, as the life span of an implant depends on what it is and how you live your life, but generally speaking, they last for a very long time—much longer than they used to. For major joint replacements, which see a lot of use, here are the general expectations:
Implants used to fix fractures, like plates and screws, are often intended to be permanent, or they might be removed after the bone is fully healed, depending on the surgeon's choice. Dental implants are often permanent and designed to last a lifetime. The key factors that impact longevity are:
Even if an implant wears out, it doesn't mean a disaster. It means you may need a second operation, called a revision surgery, to replace the worn components. 
Material Composition, Specific Cases, and Corrosion Concerns
What Are Metal Implants Made Of?Metal implants aren't just made from any old metal; they are constructed from high-grade, very specific materials that are rigorously tested to ensure they can survive inside your body for decades without breaking down. These materials have to be strong enough to bear your weight and compatible enough not to trigger a hostile immune response. The three main categories of materials you’ll hear about are:
These materials are what make the whole process possible, allowing the implant to function as a seamless, internal replacement part.
Can Cochlear Implants Go Through Metal Detectors?A cochlear implant is a specific and unique case because it is a complex electronic device, not just a simple piece of metal. It has both external components (worn behind the ear) and internal components that are surgically placed under the skin.
If you have a cochlear implant, it’s even more important to carry your identification card and to calmly notify security staff before you walk through the detector. They will likely use a handheld wand, but you should also be prepared for them to check the device and the associated documentation. For security screenings, the external sound processor and coils should be removed and screened separately, just like a phone or laptop.
Can Metal Implants Cause Infection?No, the implant material itself does not cause an infection. Infections are caused by bacteria. However, the implant can provide a surface where bacteria can stick and grow, making the resulting infection very difficult to treat. The risk of infection comes primarily from two sources:
The risk is relatively small, but because an implant infection is so serious (often requiring a second surgery to remove the device), surgeons are very proactive about prevention. You can help by taking antibiotics exactly as prescribed after surgery and telling any future doctors or dentists that you have an implant if you are getting a procedure that could release bacteria into your blood.
Do Metal Implants Rust?The short answer is a definitive no, modern metal implants do not rust in the way an old iron fence would. The word "rust" typically refers to the corrosion of iron when it’s exposed to oxygen and water. The materials used for medical implants are selected specifically because they are highly resistant to corrosion in the harsh, salty, watery environment of the human body.
If a metal did rust or corrode inside your body, it would release tiny particles and ions that would cause a severe inflammatory reaction and potentially damage the surrounding tissue. Because implant safety relies on them lasting for decades without changing, the engineering and material science behind preventing corrosion is one of the most important aspects of their design.
|